Educational Activities Building
| |
| Home |
| Biography |
| Building Statistics |
| Thesis Research |
| Thesis Proposal |
| Presentation |
| Final Report |
| Reflection |
| Senior Thesis e-Studio |
Building Statistics
Building Statistics 1
General Building Data
Building name: Educational Activities Building (EAB)
Location: PSU Harrisburg Campus, Harrisburg, PA
Building occupant name: PSU Harrisburg Campus
Occupancy type: Educational, with some engineering laboratories and offices.
Size: 55,057 GSF
Number of stories: 2 stories
Construction dates: 02/04/2013 to 05/30/2014
Total project cost: $19.4 Million
Project delivery method: CM at Risk/ Guaranteed Maximum Price
Project team:
Role
Organization
Website
Owner
Penn State
www.opp.psu.edu
CM
Reynolds Construction
www.reynoldsconstruction.com
Architect
Bohlin Cywinski Jackson
www.bcj.com
Structural Engineer
Hope Furrer Associates
www.hfurrer.com
MEP Engineer
IES
www.ies-pa.com
Civil Engineer
Raudenbush
www.raudeng.com
BIM Consultant
Adept Project Delivery
www.adeptprojectdelivery.com
Architecture
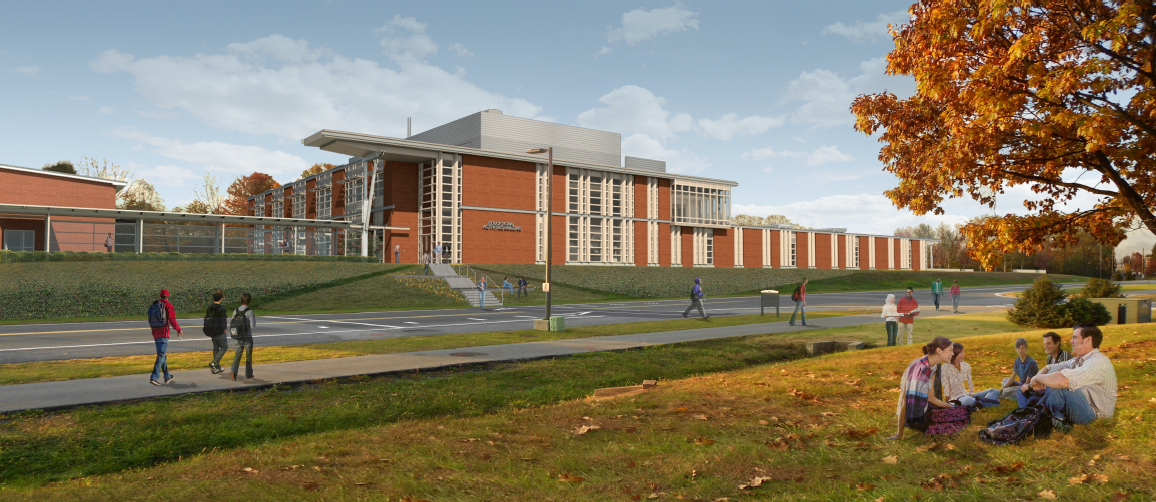
The Educational Activities Building addition is a 51,000 square foot project located on the Penn State Harrisburg Campus. The building will be used for classrooms, laboratories and offices for the different programs offered at the Harrisburg Campus. The structure is L- shaped with curtain wall façade covered with brick veneer. The short side of the building consists of two floors and the long side is mostly one floor. The site of the project doesn’t have any historical significance which eliminates any historical requirements or regulations.
The project is located within the campus property line so it follows the Educational-Institutional Zoning District (E-I). Some of the zoning regulations are as follow:40’ maximum building height.
75’ front yard setback from street or driveway center line.
Codes:
IBC- International Building Code, 2009
International Fire Code, 2009
International Energy Conservation Code, 2009
International Existing Building Code, 2009
International Fuel Gas Code, 2009
International Mechanical Code, 2009
International Plumbing Code, 2009
International Urban-Wildland Interface Code, 2009
International Code Council, 2003Building Enclosure
Building Façade:
the building exterior is made of Aluminum Curtain Wall system. The walls are covered with brick veneer on the outside and 1” insulated glazing unit on the inside. The curtain wall is connected to the ground with 4” CMUs with ½” exterior gypsum sheathing. In addition, glazed aluminum channels are used around the openings in vertical sections of the building.Roofing:
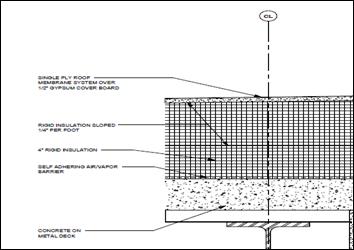
The roofing mainly consists of a single ply roof membrane system over ½” gypsum cover board. Additionally, there’s a layer of 4” of rigid insulation between the membrane system and the roof structure. Finally, a self-adhering air/vapor barrier is placed between the 4” insulation and the concrete on metal deck roof.
Sustainability Features
Mechanical system sustainability features:
- The HVAC system is central station air handling unit, which utilizes chilled water for cooling and hot water for heating.
- Variable volume supply and return fans using variable frequency drives on the motors.
- Energy recovery wheels which recover sensible and latent energy from relief and exhaust air.
Electrical system sustainability features:
- Electrical distribution includes various step-down transformers.
- Majority of the lighting in the building are LED lighting with lighting control based on localized sensors.
Building Statistics 2
Construction:
The location of the Educational Activities Building is adjacent to an old existing building and one access road First Street. There is enough space for the construction site as seen in the bird’s eye view of the location (Figure2). However the existing building will be occupied by students and faculty during construction, which the project team took into consideration. The First Street is used as the main entrance and exit with two gates located on the south and north.
The project team was fully aware and familiar with the climate of this region and they did proper planning to avoid weather delays when creating the construction schedule. The site was bare with the exception of few trees that had to be removed before the beginning the excavation process.
The building is divided into two construction areas: south wing and north wing. That accelerates the construction work and makes it more efficient. The foundation started in the south wing followed by the north wing. With the same coordinates, the slab-on-grade was poured and the steel frame was erected after the curing of the concrete from the ground up. The metal decking with concrete elevated slab was built from top to bottom, starting from the roof and moving down to the second level. As the metal decking and the concrete elevated slab was done for each floor, the MEP rough-in and finishes began. Those activates overlap each other for each floor. Additionally, there was overlap on different activities occurring simultaneously between the south wing and north wing.
Electrical System:
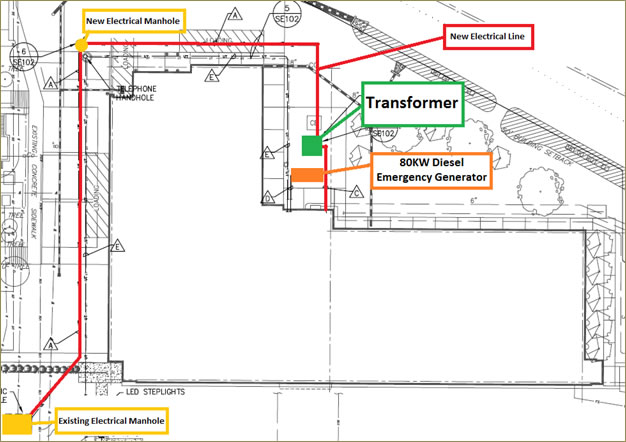
The electrical service to the building is 1600A, 480V, 3 phase, 4 wire service and comes from a manhole located on the east side of First Street. It gets to a transformer located outside of the building then it enters through the west side of the first floor of the north wing where the only electrical room is located. The service then proceeds to a switchgear that distributes the power to sub-distribution panels and transformers. The electrical distribution includes various step-down transformers, distribution panels and branch panels located throughout the building to supply power to the different equipment. There is 80KW diesel emergency generator located outside the building next to the transformer and it is used to provide life safety loads and other miscellaneous loads in the event of a power outage. Figure3 will help identify the locations of the different components of the electrical system.
Lighting System:
The building majority lighting system is LED lighting including recessed 1’x4’ for the classrooms and labs and 3” wide linear LED fixtures and LED downlights for the corridors. The fluorescent fixtures are utilized for the lab wing corridors. The lighting control system is based on a localized Creston GLPAC units placed on the ceiling of each region. The regions consist of either 4 or 8 zone units. Although, the laborites typically have 3 zones with an occupancy sensor and photocell to provide daylight harvesting.
Mechanical System:
The mechanical system is a central station air handling unit which utilizes chilled water for cooling and hot water for heating. The mechanical room is located on the first floor of the north wing right next to the electrical room. The system consists of a 200 ton cooled chiller to produce chilled water located on the roof. A screw compressor is used to control the capacity from 100% to 10% of the load. This is beneficial to supply the correct amount of chilled water and temperature needed for the most demanding zone in the building. The system has 4 air handling unites and equipped with total energy recovery wheels to exchange sensible and latent energy between the exhaust air and the incoming outside air. All four units are located inside the penthouse.
Structural System:
The foundation consists of 8” CMU foundation walls and cast in place concrete footings ranging in size from 3’x3’ to 12’x39’. The slab-on-grade is made out of 3500 psi normal weight concrete with a thickness of either 5” or 6”. The reinforcement steel for the slab-on-grade utilizes 6x6-W2.9xW2.9 welded wire mesh. The composite metal decks are covered with a 3.25” layer of 3500psi lightweight concrete and 6x6-W1.4xW1.4 welded wire mesh. The structural system is made of steel framing. The beams and girders are mostly wide flange beams ranging from W8x15 to W30x90 with a few HSS and C beams. Beams run from south to north, while girders run from east to west. Likewise, columns are generally wide flange beams ranging from W8x21 to W10x100 and few HSS. Certain columns extend throughout the building height and some extend for one or two floors. The columns are spaced with a typical pattern scheme.
Fire Protection:
The building utilizes an active wet pipe fire protection system. Sprinkler heads are distributed throughout the building with a maximum coverage of 225 square foot. Additionally, portable fire extinguishers are provided in different areas of the building. The fire resistance rating for the stairways, stairways doors and elevator shafts is one hour.
Transportation:
The building has two sets of staircases one located in the 2 levels part of the north wing and one on the east side of the south wing. This eases traveling by the occupants between the building levels. There is one elevator placed in a centralized location between the two wings.
Telecommunications:
The Educational Activities Building contains rooms with projectors, screens and a computer to control the system. The computer labs in this building will contain desktops, printers and other equipment.For a PDF file of the assignments please click on the images below:
| Senior Thesis Main Page |
| Penn State |
| AE Department |
| AE Computer labs |
| Contact Meshal |
©2013"