General Building Information |
Building Name: |
Southwest Student Housing | 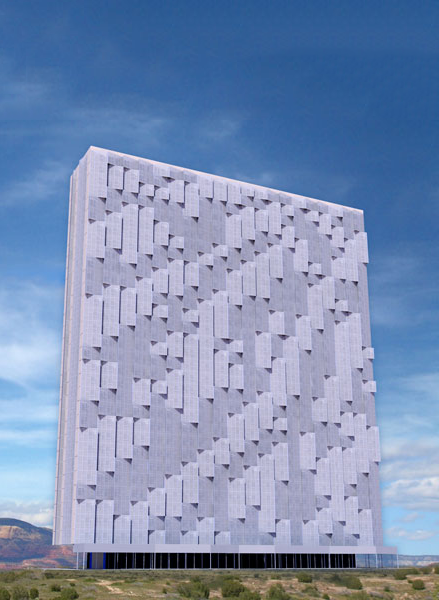
click the images to see a bigger version |
Location: |
Tempe, Arizona |
Occupancy:
|
Arizona State University students; R-2- Residential, more than 2 units (268 units, 528 beds). S-2- Enclosed Parking Garage |
Size: |
280,900 square feet |
Number of Stories: |
20 above grade, 0 below grade |
Cost:
|
Direct hard costs- $30 357 459
Contractor total, no contingencies- $34 420 280
Total cost- $37 358 413 |
Dates of Construction: |
TBD. Construction time- 8 months |
Project Delivery Method: |
TBD. Most likely Design-Build |
Project Team:
|
Owner- Arizona State University (www.asu.edu)
General Contractor- TBD
Project Delivery- Romani Group (www.romanigroup.com)
 Thornton-Termohlen Group (www.ttgcorporation.com) Thornton-Termohlen Group (www.ttgcorporation.com)
Architecture- BOKA Powell (www.bokapowell.com)
 De Vido Architects (www.devido-architects.com) De Vido Architects (www.devido-architects.com)
Structural Consultant- Thornton Tomasetti (www.thorntontomasetti.com)
MEP Consultant- WSP Flack and Kurtz (www.wspfk.com)
Contractors:
 Steel- Star Seismic (www.starseismic.net) Steel- Star Seismic (www.starseismic.net)
 L.P.R. Construction Co. (www.lprconstruction.com) L.P.R. Construction Co. (www.lprconstruction.com)
 Concrete- Bang Concrete (no website) Concrete- Bang Concrete (no website)
 External Wall- Precision Wall (no website) External Wall- Precision Wall (no website)
 Prefab Bathrooms- Eggrock, LLC (www.eggrock.com) Prefab Bathrooms- Eggrock, LLC (www.eggrock.com)
 Slipform and Lifting- Scanada International, Inc (www.scanada.com) Slipform and Lifting- Scanada International, Inc (www.scanada.com)
 Fasteners/Firestop- Hilti North America (www.hilti.com) Fasteners/Firestop- Hilti North America (www.hilti.com)
|
Architecture |
Major Codes:
|
International Building Code (2006)
International Energy Code (2006)
International Fuel Gas Code (2006)
International Mechanical Code (2006)
International Residential Code (2006)
International Plumbing Code (2006)
National Electric Code (2006)
Tempe Building Safety Administrative Code (2005)
International Fire Code (2006)
Zoning and Development Code of the City of Tempe, Arizona (2010)
|
Zoning:
|
Zone district MU-4 (PAD)- Mixed-use, High Density Planned Area Development
Permit required for parking facilities, no permit required for residential construction; No standard for building height or density; Building step-backs required only on boundaries with zoning district SF or MF; Setbacks- none for building walls, 20' on front and street side for parking facilities; No lot coverage requirement, or landscape area requirement. |
Historical Requirements: |
None on this project |
Design:
|
The SW Student Housing building is a modern 20 story high-rise for students attending Arizona State University that gives residents an extensive view of the city of Tempe, Arizona. The narrow footprint of this building encompasses three concrete cores built around the elevators and stairwells. Navigation through the building is along a central hallway running through the entire length of each 14,000 square foot level. 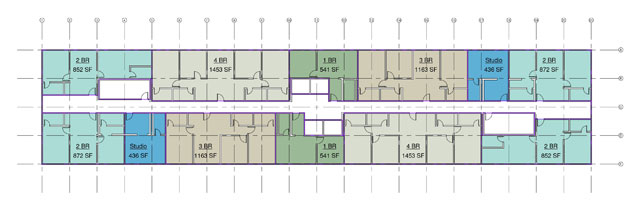
Each of the 528 bedrooms has access to its own prefabricated bathroom complete with a toilet, vanity and shower. The bedrooms are arranged in groups of one, two, or four. Each of these 268 groups shares a living area, mimicking a typical apartment layout, and includes living, kitchen and laundry amenities. Each corridor and living space will be carpeted, with linoleum tile in the kitchen. The ceiling in the living areas will show the exposed structure of the floors. The wall finishes throughout the building will consist of painted drywall, with hung acoustic tile ceiling in the corridors. There will also be a pleasant finished elevator lobby on the ground floor.
|
Building Enclosure |
|
Though a definitive design for the exterior facade has yet to be chosen, the materials 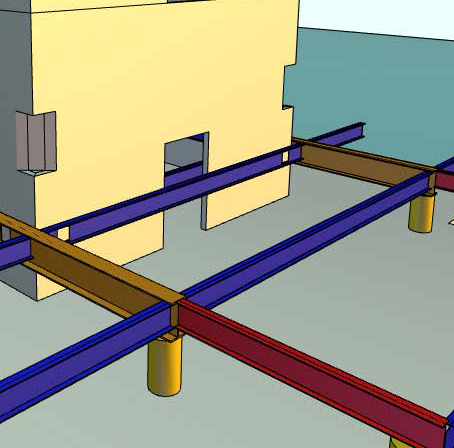 for the facade are already known. The entire building will be enclosed in a panelized exterior insulation and finish system (EIFS), excluding the first floor. The exterior wall of the ground floor will be aluminum and glass. for the facade are already known. The entire building will be enclosed in a panelized exterior insulation and finish system (EIFS), excluding the first floor. The exterior wall of the ground floor will be aluminum and glass.
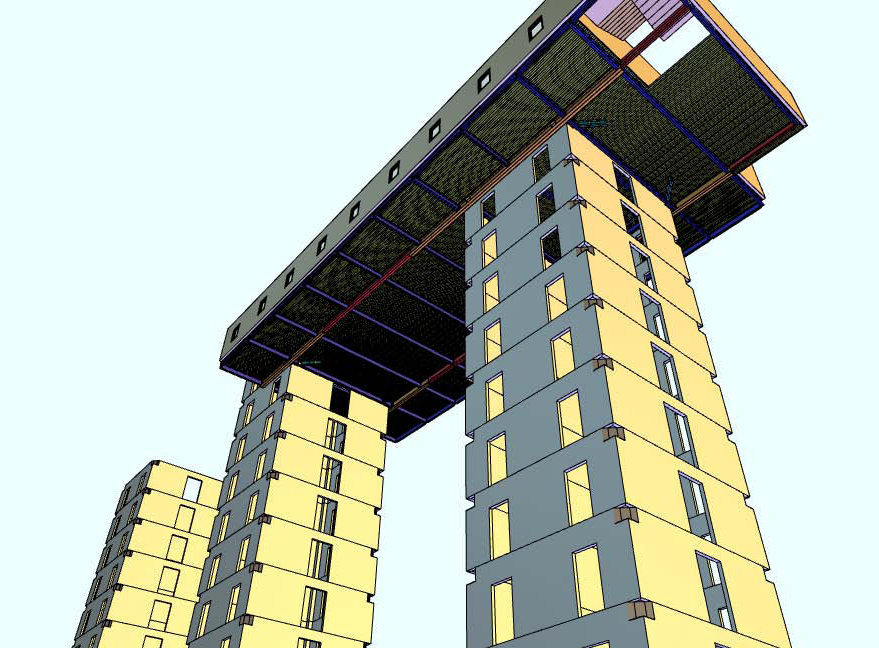
The structure for the roof will be provided by a cambered structural steel frame that will be assembled on the ground and raised into place, one half of the roof at a time, using string jacks attached to the tops of the three concrete cores. The roof covering will consist of Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer (EPDM) - a rubber roofing membrane designed for roofs with a low slope. Please note- the image at right is indeed the roof structure, but the roof (and every floor) will be assembled on the ground and raised into place. |
Sustainability Features |
|
The goal in the construction of this building is to use as many prefabricated items as possible. In using modular design, the engineers have managed to come up with a building that takes two thirds less time to build, with a cost reduction of one third from conventional construction. Additionally, the amount of concrete used is about half of what would be required for constructing this type of building using conventional methods. As a result, this building has several inherent sustainability features in its construction. Less concrete means that this building will require less Portland cement, which is a major player in a building's carbon footprint. Modularity and fast construction allows for heavy construction machinery to be removed from the site earlier, causing less damage to the surroundings. Additionally, the method of construction (slip-form concrete cores) eliminates the need for high tower cranes and gratuitous quantities of plywood for concrete forms.
|
 |


 Building Statistics
Building Statistics














