Building Statistics
Building Statistics
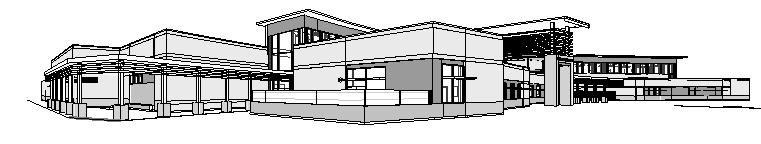
Building Name: Cypress Hill Elementary School
Location and Site: Bridgeport, Texas
Building Occupant Name: Cypress Hill Elementary
Occupancy: Educational, occupancy type "E"
Size: 105,529 square feet for the school, 9,377 square feet for gymnasium
Floors above grade: 2 levels
Owner and primary project team withheld by request.
Dates of construction: September 7, 2012 to November 26, 2013
Project delivery method: Design-build
Actual cost information: $82.3 Million with construction
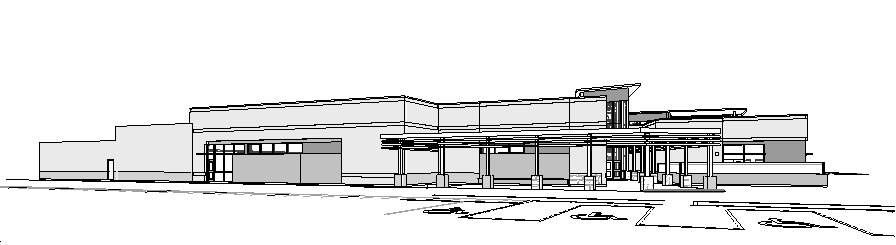
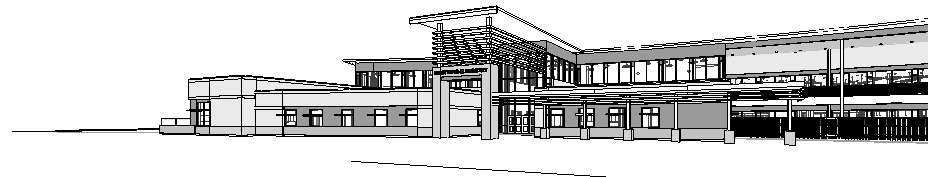
The old Cypress Hill Elementary stood on the same site but was demolished to construct the new Cypress Hill Elementary. The new school features a whole new footprint and shares nothing with the old school. In addition to the new school, there was also the addition of a detached gymnasium on the same site. Cypress Hill was built to facilitate children in pre-kindergarten through fifth grade taking children ages 4 and up. The designed occupancy count is 800 students and 75 members of the faculty. The school goes up to a second floor that is not consistent throughout. The second floor connects by mezzanine. Inside the school there is a library for study and recreation along with music facilities. The cafeteria comes equipped with a stage and doubles as a performance area. The architecture is fairly modern with a sloping south façade. It is mostly steel construction with some masonry for veneer. The style is eclectic in its changing ceilings in many spaces. The stone finishes set it apart from other buildings in the area. The school is located in the middle of the suburbs so a nicely furnished school becomes something more in this atmosphere. The school district knew they needed a new school in late October 2011. A representative for the district contacted an architect who worked in tandem with an MEP firm and a structural firm to design and build the school. The new Cypress Hill elementary is currently under construction.
The major codes used during design were 2006 International Building Code, 2006 International Fire Code, 2006 Uniform Mechanical Code, 2006 Uniform Plumbing Code, 2011 National Electrical Code, 2009 International Energy Conservation Code, ASHRAE 90.1-2007. There are no zoning requirements in the Texas town where the school is located and there is no applicable historical district where it is located.
The roofing is liquid rubber white EPDM roof coating, applied over 2" tapered insulation over 2" lightweight concrete over 4" rigid insulation on vented metal deck.
The façade is a combination of glacier white brick and 60% dark ironspot velour 40% medium ironspot velour. Fiber cement paneling is used between windows. The fascia, risers, stair stringers, and soffits are pre-finished metals with matte finish paint. There is also a 2' limestone veneer around the lower perimeter of the school.
The main goal was to build a building that lasts and is comfortable for the students inside so sustainability was not the largest concern; however, there are a number of sustainable design features. One of the largest components of this is the glazing that is seen throughout the façade and the building itself. There are also a number of light shelves and clerestory windows. The building focuses on passive solar and daylighting.
The structural system for Cypress Hill Elementary is primarily a steel beam column system with diagonal bracing for lateral loads. Underneath the school, the foundation is concrete piers that go down 7' to 19'. The piers are typically placed every 5' around the perimeter of the building and sporadically throughout. The first floor is 5" thick high strength concrete slab on grad. The second floor used k-series floor and roof joists at a span of 5' with a slab on a metal deck floor. The size of the steel structural columns range from HSS10X10X1/2 to HSS6X6X1/4. The roof was constructed using 16 K-series joists supporting 15/16" 24 GA vented metal deck.
Power from the utility is dropped down to 277Y/480V by an external pad mounted transformer. Power goes to the main distribution panel rated for 3000 amps which distributes 277Y/480V to 10 277/480 panelboards. These panelboards feed 10 low density power panelboards at 120/208V through a step down transformer. The 277/480 panels also serve relay panels for lights. Should power fail, an automatic transfer switch is in place for a 175kW/218kVA natural gas generator to power up and emergency panels will take over via relays to serve the building's power. The detached gym uses overhead power and transformers from the utility to serve 480/277V with a step down transformer for 120/208V. The total connected load for the school is approximately 1060 KVA. There are 15 emergency panels connected to both the main distribution board and the gas generator. The total connected emergency load is approximately 75 KVA.
The school is served mostly by ten variable air volume (VAV) air handling units. Four other single zone constant volume air handling units (AHU) with variable frequency drives (VFDs) serve special areas like the kitchen, cafeteria, media center, and the detached gym . Dual duct mixing boxes are used in different zones throughout the school. Some areas like stage storage, MDF room, along with some spaces with may be used after hours, are served by dual expansion fan coil units while a fan coil unit serves the corridor. Two 226 ton chillers serve the entire school.
The large areas like the media center, cafeteria, corridor, and vestibule, all use a similar design with fluorescent pendant luminaires of different sizes and heights used for the main illumination of the space. Besides those, most luminaires in the school are recessed compact fluorescent downlights. Emergency luminaires are circuited to emergency power via relays. Although the building's luminaires mostly use fluorescent lamps there are metal halide downlights in the media center because the ceiling is double height and incandescent luminaires serving the stage area in the cafeteria. Occupancy sensors are utilized in common spaces like work areas. The current site lighting is pole mounted LEDs.
In late 2011 the Cypress Hill school district decided to demolish the old school and build a new one on the site. The construction for the new school broke ground on September, 7 2012. The project delivery system is a design-build project and is scheduled to be completed in November 26, 2012. Durotech from Houston was hired for the construction process. The existing gym was not touched during the demolition process and it will not be renovated to match the new school.