| Home |
| Biography |
| Building Statistics |
| Thesis Abstract |
| Technical Assignments |
| Thesis Proposal |
| Presentation |
| Final Report |
| Reflection |
| Senior Thesis e-Studio |
General Building Data |
|
Building Name:
Location and Site:
Building Occupant:
Occupancy Type:
Building Size:
Number of Stories:
Project Team:
-Owner:
-General Contractor:
-Architect of Record:
-Architectural Partnership:
-Structural Engineer:
-MEP Engineer:
-Civil Engineer:
Dates of Construction:
Construction Cost:
Project Delivery Method:
Office Building
Sayre, PA
Withheld at Owner's Request
Business
85,075 SF
5 (all above grade)
Withheld at Owner's Request
High Construction Company
Silling Associates, Inc.
Elliott + Associates Architects
Larson Design Group
Larson Design Group
Larson Design Group
March 2012 - April 2013
$11 Million
Design-Bid-Build
Architecture |
The footprint of the Office Building is laid out in an off-centered "H" configuration with an east and west wing joined together by a shorter, perpendicular central portion. This connecting section of the building is offset from the centers of the wings to the south. Both wings are comprised primarily of office space while the central portion acts as the main circulation core and meeting area. Additionally, a fitness area and locker rooms for employees are featured in the east wing on the second floor. The 6' high horizontal glazing strips that run along the entire perimeter of the building allow ample amounts of sunlight to penetrate deep into the building. A prominent parapet extends up past the roof to a maximum height of 74'-5" along the east and west facades. It then tapers down to a height of 68'-2 1/2" at the interior edge of the wings and continues at this elevation across the connecting middle segment of the building.
Major National Building Codes:
-International Building Code 2009
-ASCE 7-05
-International Mechanical Code 2009
-International Plumbing Code 2009
-International Fuel Gas Code 2009
-International Fire Code 2009
-NFPA 13
-NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) 2011
-NFPA 72 (National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code) 2010
-NFPA 101 (Life Safety Code) 2009
Zoning: Request has been made for further zoning information.
Historical Requirements: N/A
Building Enclosure |
Facade:
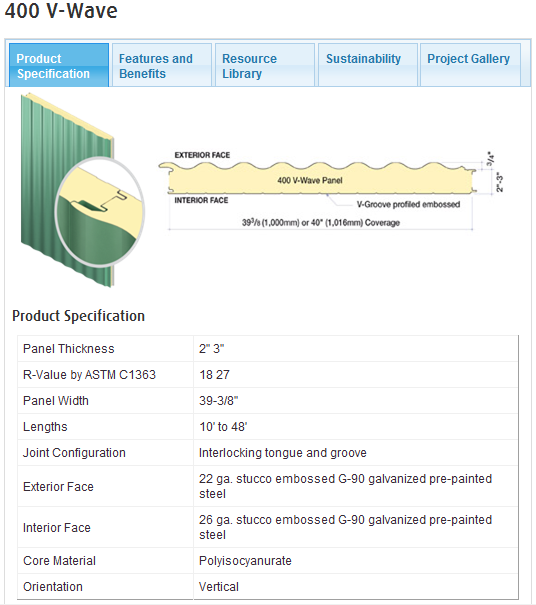
The east and west wings of the Office Building are enclosed by 2" thick Kingspan-400 Series V-Wave insulated metal panels over a weather resistive barrier on 1/2" sheathing on 6" metal studs at 24" OC with batt insulation infill between studs. 5/8" gypsum wall board is fastened to the inside face of the studs. See Figures 1 and 2 for details.
The solid façade is broken up by horizontal strips of Kawneer 451T storefront glazing. This glazing system is comprised mainly of 1” insulated units made up of 1/4” clear tempered outside pane with low-e coating, 1/2” air space with argon and 1/4” gray tempered inside pane. These units are broken up at the column grid lines by 1” insulated units made up of 1/4” clear outside pane, 1/2” air space with argon and 1/4” spandrel panel.
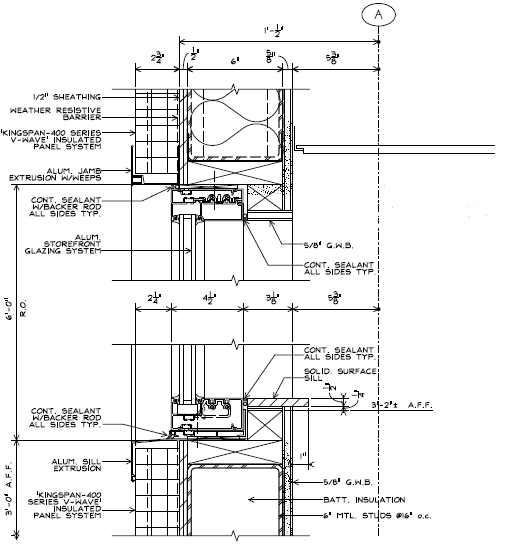
Figure 1: Typical Wall Section Detail
(Image Credit: Silling Associates, Inc.)
Figure 2: Insulated Metal Panel Specification
(Image Credit: Kingspan Insulated Panels)
The central portion of the building connecting the north and south wings is enclosed with a Kawneer 1600 curtain wall glazing system comprised of the same two types of 1” insulated glazing units as described above for the north and south wing facades. See Figure 3 for details.
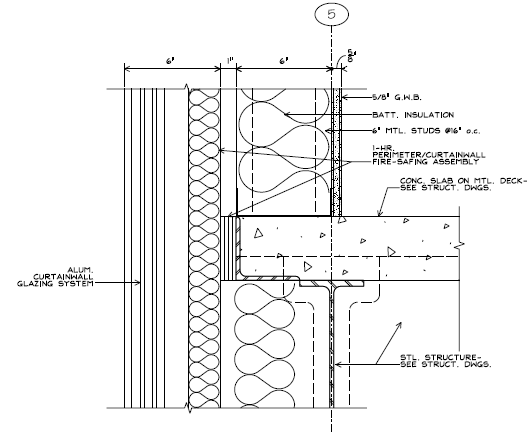
Figure 3: Typical Curtain Wall Section Detail
(Image Credit: Silling Associates, Inc.)
Roof:
The roofing is made up of fully adhered EPDM roof membrane on 4” thick (max) rigid roof insulation (minimum R-20). The rigid insulation is supported by 1 1/2” metal roof deck on open web steel joists. See Figure 4 for details.
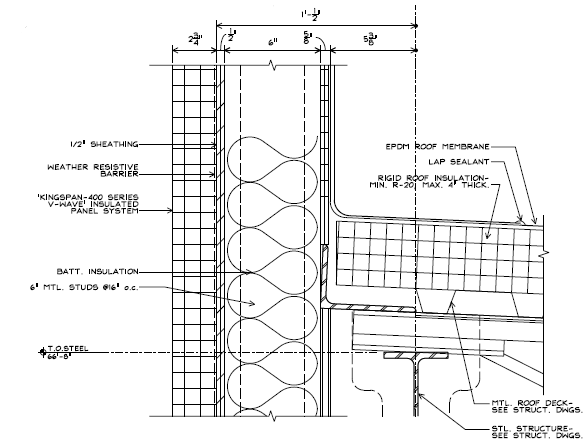
Figure 4: Wall/Roof Section Detail
(Image Credit: Silling Associates, Inc.)
Sustainability Features |
The low-emissivity coating on the glazing unit panes serves to block a significant amount of radiant heat transfer through the glass while still allowing visible light to pass through into the interior of the building. Reducing solar heat gain is important to reducing the overall cooling loads that will be placed on the mechanical system. In addition, the glazing units have a 1/2” airspace filled with argon. Argon provides better insulation performance than a typical airspace would offer since it is less conductive and more viscous than air.
The Kingspan-400 Series V-Wave façade panels have a continuous rigid insulation core and offer a minimum R-18 value for superior insulation performance. The exterior skins are made from a significant portion of recycled material and the overall panels are recyclable. The insulated metal panels are made from recaptured metals and weigh only 3 PSF, which reduces the energy to transport and install them significantly.
Building Systems |
Structural:
The primary superstructure of the Office Building is constructed of wide flange structural steel beams and columns. The first story floor is a 4" thick slab-on-grade. Floors 2-5 consist of 2 1/2" thick normal weight concrete topping on 20 gauge 1 1/2" composite deck. The composite deck slab is supported by open web steel joists, typically 16K2 up to 16K4, spaced at 3'-0" on center, maximum. Floor loads are then distributed to the wide flange beams. Interior beams are typically W24x and exterior beams range from W12x to W16x. Steel beams carry the loads to wide flange columns, typically W12x53, W12x65, W12x79 and W12x106. The roof is made up of 1 1/2" Type B 20 gauge wide rib roof deck supported primarily by 16KCS2 and 24K4 open web steel joists spaced at 6'-0" on center, maximum.
The structure is founded on spread, combined and strip footings that support concrete piers, pier walls, foundation walls and columns directly to transfer loads from the superstructure to the soil they bear upon. Lateral forces are resisted by 16 "K" braced frames, 8 in each the N-S and E-W directions, which extend up to the roof of the building. The frames are typically braced by 2L6x3 1/2x5/16 LLBB double angles at locations above and below the windows at each story.
Electrical:
Power for the Office Building enters the main electrical room at the northwest corner of the building on the first floor. A 2000 A, 480 V, 3-phase NEMA 3R fused main disconnect is located outside the building and receives the incoming service from the utility transformer. Power runs inside to the main electrical room through a 2000 A automatic transfer switch provided for the emergency generator backup system. The 480/277 V, 3-phase, 4-wire main distribution panel then supplies the lighting panels directly at each floor with 480/277 V power. There are four lighting panels on both the first and fifth floors and two lighting panels on floors 2-4, split between the east and west wings. Two 112.5 kVA transformers on each floor step the 480 V from the main distribution panel down to 208Y/120 V to feed the power panels. There are four power panels on each floor, with two typically serving each wing of the Office Building at any level.
Lighting:
Lighting in the Office Building is predominantly fluorescent and operates at 277 V. Typical fixtures in the office, corridor and meeting spaces include recessed Lithonia 2'x4' volumetric and prismatic troffers. These fixtures are each equipped with two T5 fluorescent lamps. Compact fluorescent downlighting in the lobby spaces is provided by recessed Gotham can lights equipped with horizontal triple-tube lamps. Emergency lighting is primarily provided by recessed Lithonia 2'x4' volumetric troffers, also with T5 lamps.
Mechanical:
The Office Building is serviced by ten 10-ton Mitsubishi condensing units, located on the roof of the structure. Also on the rooftop are two Carrier 7000 CFM energy recovery ventilators (ERVs). The ERVs utilize wheel exchangers for both heating and cooling and achieve approximately 75% heating/cooling efficiency. Two 25 kW electric duct heaters provide supplementary heat and are located in mechanical rooms on the fifth floor. Each story is serviced by between 31 and 39 Mitsubishi air handling units (AHUs), ranging from 120-635 CFM. The majority of AHUs are concealed, ducted units while the others are either ceiling or wall mounted. Two 310 CFM Reznor electric unit heaters are used for localized heating, with one in the fire riser room on the first floor and the other in the large first floor storage room at the north end of the building's west wing.
Fire Protection:
The construction type for the Office Building is Type IIA. The primary structural frame, which includes columns, members connected to the columns and bracing members, has a required fire rating of 1-hour. Floor and roof construction and secondary structural members also have a 1-hour fire rated requirement. Sprayed-on cementitious fireproofing is specified for all structural system elements, including application to the bottom of the deck. Stair and elevator shaft supporting structural elements require a 2-hour fire rating, as does the shaft wall system enclosing the stairs and elevators. A 6" combined standpipe and riser is located in the western stair and a 4" standpipe in the eastern stair to serve each wing of the Office Building. The building is fully sprinkled by concealed pendant sprinkler heads, each providing a coverage of 225 square feet.
Circulation:
Circulation in the Office Building is provided by two stairwells, one located at the south end of both the east and west wings, and two elevators centrally located in the connecting portion of the building. The ThyssenKrupp Synergy 300E model 4500 elevators have a rated capacity of 4500 pounds and an operating speed of 350 ft/min. The elevators are gearless traction, machine room-less passenger type with 4' wide by 7' tall door openings. The clear interior cab dimensions are 5'-8" wide by 7'-9 1/2" deep by 8'-0" high.
Construction:
The delivery method is Design-Bid-Build for the Office Building project in Sayre, PA. High Construction Company, as the general contractor, was awarded Phase 4 of the multi-phase office complex development project at an approximate construction cost of $11 million. With work starting in March 2012 and an anticipated completion date of April 2013, the duration of construction for the Phase 4 office facility is just over one year. In addition to the Office Building, Phase 4 of the project includes the construction of a metal shop building, located just north of the office facility on the same site.